Cancer is one word that no one wants to hear. It can bring a lot of fear and confusion to many families who have a memberdiagnosed of cancer. Usually, it is more seen in adults, but in recent time, cancer has also been diagnosed in children, and even too. Very often if it happens in kids, it can be treated and cured.

Cancer is simply a disease of the cells, where bad cells multiply themselves and grow into tumors and even affect all other body organs. There are many types and kinds of cancer.
But cancer is a huge issue everywhere in the world today. It is also very technical (which means it is not easy to understand). Even though there are great advancements in cancer management, there is still a lot of research going on with cancer to find out more about it.
It was also found that in 2009, €51·0 billion (40%) of healthcare cost was for cancer.
Lung cancer had the highest economic cost (€18·8 billion, 15% of overall cancer costs), followed by breast cancer (€15·0 billion, 12%), colorectal cancer (€13·1 billion, 10%), and prostate cancer (€8·43 billion, 7%). Source: The Lancet Oncology, Early Online Publication, 14 October 2013
In this lesson we shall look at some basic information on cancer, how it develops, some signs and symptoms that we can look out for, what we can do to reduce our risk and some general information and statistics about it. There are notes on the left column which explains some technical terms.
Enjoy the lesson.
What is cancer, and how does it develop?
The organs in our body are made up of cells. Cells don’t just appear from anywhere in our body. They are produced by an existing cell copying itself and splitting to produce two new cells. This is calledcell cycle. This cycle is tightly controlled and it only happens if the body needs to replace worn out cells. When these cells continue multiplying even when the body doesn't need them, the result is a mass or growth, also called a tumor.
Illustration of normal cells dividing
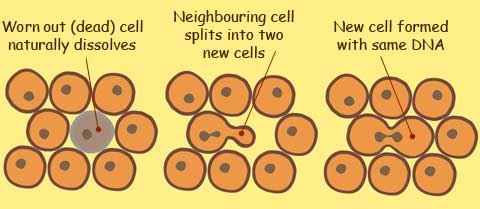
Illustration of uncontrolled multiplication of abnormal cells

These growths are considered either benign or malignant. Benign is considered non-cancerous and malignant is cancerous. Benign tumors rarely are life threatening and do not spread to other parts of the body. They can often be removed.Malignant tumors, however, often invade nearby tissue and organs, spreading the disease.
Cancer can be life threatening. The key is in early diagnosis. If cancer is diagnosed early, there is a high chance that the cancer can be completely cured.
How Does Cancer Spread to
Other Parts of the Body?
The cells within malignant tumors have the ability to invade neighboring tissues and organs, thus spreading the disease. It is also possible for cancerous cells to break free from the tumor site and enter the bloodstream, spreading the disease to other organs. This process of spreading is called metastasis.
What causes cancer?
What causes tumors? What conditions make cancer-development easy? What are the cancer risk factors? Good questions.
There is not a single answer for this, but experts know that cancer is not contagious, and isn't caused by germs, like colds or the flu. There is a kind that is caused by a virus from unsafe sexual activity, but we will look at that later. Do not be afraid of other people with cancer.
Each cancer type is different and that means the causes vary. For example, lung cancer may be caused by inhaling tobacco smoke, or toxic chemicals. Inhaling the same chemicals will not give you cervical cancer. In the same way, exposing your skin to intense sunlight can cause melanoma (skin cancer) but can never give you lung cancer. With this in mind, let us see a few general causes of cancer.
What causes tumors? What conditions make cancer-development easy? What are the cancer risk factors? Good questions.
There is not a single answer for this, but experts know that cancer is not contagious, and isn't caused by germs, like colds or the flu. There is a kind that is caused by a virus from unsafe sexual activity, but we will look at that later. Do not be afraid of other people with cancer.
Each cancer type is different and that means the causes vary. For example, lung cancer may be caused by inhaling tobacco smoke, or toxic chemicals. Inhaling the same chemicals will not give you cervical cancer. In the same way, exposing your skin to intense sunlight can cause melanoma (skin cancer) but can never give you lung cancer. With this in mind, let us see a few general causes of cancer.

Every person inherits some genes from their parents. If you inherit an abnormal gene (called a mutation), there is a 10% chance that, that abnormal gene will help cancer formation if the conditions are right. Specialists call this genetic predisposition. Breast cancer genes are examples of genetic predisposition. Women who carry one of these abnormal genes have a higher chance of developing breast cancer than women who do not.
Secondhand smoke is a known human carcinogen. Tobacco smoke contains more than 7,000 chemical compounds. More than 250 of these chemicals are known to be harmful, and at least 69 are known to cause cancer.

No, age does NOT cause cancer (laugh)
Sometimes the changes that make a cell become cancerous in the first place take a long time to develop. There has to be a number of changes to the genes within a cell before it turns into a cancer cell. These changes can happen by accident when the cell is dividing. Or they can happen because the cell has been damaged by carcinogens and the damage is then passed on to future cells when that cell divides. The longer we live, the more time there is for genetic mistakes to happen in our cells.
People who have problems with their immune systems are more likely to get some types of cancer. Example, people with organ transplant, people living with HIV or AIDS or even people with rare medical syndromes which affect their immunity. Some cancers such as cervical cancer and other cancers of the genital or anal area, some lymphomas, liver cancer and stomach cancer. Lymphomas are caused by viruses. This means that with a low immune system, viruses attacking your cells are able to divide without control and are more likely to develop genetic faults and develop intolymphomas.
Many people in the western world eat too much red and processed meat and less fresh fruit and vegetables. This eating habit is known to increase the risk of cancer. Drinking alcohol can also increase the risk of developing some types of cancer.
Recent studies have shown that people who have helicobacter pylori (H pylori) infection of their stomach develop inflammation of the stomach lining, which increases the risk of stomach cancer. Infection can be treated with antibiotics, but when left for so long, it can cause damage to many vital organs and make the cells in that area vulnerable for cancer formation
There are many things and chemicals all around us that may in many little ways make us cancer prone. These include the sun, natural and man made radiation, work place hazards like chemicals and smells, asbestos and others. Some of these are avoidable and some aren't.
Viruses can help to cause some cancers. But this does not mean that these cancers can be caught like an infection. What happens is that the virus can cause genetic changes in cells that make them more likely to become cancerous.
In summary, cancer is a bit complex and no one thing is known to cause it. Keeping well, eating healthy, avoiding chemical inhaling, zero smoking, staying away from sexual activity until you are married or old enough to do so, and general personal care can largely reduce your exposure to sexually transmitted infections and minimize your risk of cancer.
Common types of cancer
There are more than 200 different types of cancer. Remember we said it is a disease of the cells? And cells make up tissues, and tissues make up organs? This means cancer can affect all your body organs: brain, blood, skin, cervix, throat, pancrease, stomach, intestines, liver, bladder, bone, testes, infact all your body organs can be affected.
Breast, lung, bowel (colorectal) and prostate - account for over half (54%) of all new cases. The most common cancer type for men is prostate cancer, whiles breast cancer is the most common in women. Below is a list of 9 most common cancer types.
 Bladder Cancer
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer develops from the transitional cells which line the inside of the bladder. The common early symptom is blood in the urine. In most cases, the cancer is confined to the inside lining of the bladder. Normal bladder cancers is relatively easy to treat. If the cancer has spread into or through the muscle layer of the bladder wall then treatment is more difficult.
 Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer
This forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages. Smoking is the cause of most cases. There are two main types: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. Non-small cell lung cancer types is more common.
 Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer
It forms in tissues of the breast, affecting the ducts (tubes that carry milk to the nipple) and lobules (glands that make milk). It largely affects women.
 Skin cancer
Skin cancer
There are two main types are: malignant melanoma (less common but more serious; and non-melanoma skin cancer, which is very common but not so serious)
It starts with cells that make the pigment melanin. Because it forms on the skin, patients are usually the first to spot the cancers on the skin.
 Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic Cancer
This type is also called exocrine cancer. The cancer cells form in the tissues of the pancreas.
 Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer
This type usually occurs in men over 50 years of age and the risk increases as you grow older. It develops in tissues of the prostate (a gland in the male reproductive system found below the bladder and in front of the rectum).
 Leukemia
Leukemia
It is commonly known as cancer of the blood. It starts in blood-forming tissue such as the bone marrow and causes large numbers of blood cells to be produced and enter the bloodstream.
There are more than 200 different types of cancer. Remember we said it is a disease of the cells? And cells make up tissues, and tissues make up organs? This means cancer can affect all your body organs: brain, blood, skin, cervix, throat, pancrease, stomach, intestines, liver, bladder, bone, testes, infact all your body organs can be affected.
Breast, lung, bowel (colorectal) and prostate - account for over half (54%) of all new cases. The most common cancer type for men is prostate cancer, whiles breast cancer is the most common in women. Below is a list of 9 most common cancer types.
Bladder cancer develops from the transitional cells which line the inside of the bladder. The common early symptom is blood in the urine. In most cases, the cancer is confined to the inside lining of the bladder. Normal bladder cancers is relatively easy to treat. If the cancer has spread into or through the muscle layer of the bladder wall then treatment is more difficult.
This forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages. Smoking is the cause of most cases. There are two main types: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. Non-small cell lung cancer types is more common.
It forms in tissues of the breast, affecting the ducts (tubes that carry milk to the nipple) and lobules (glands that make milk). It largely affects women.
There are two main types are: malignant melanoma (less common but more serious; and non-melanoma skin cancer, which is very common but not so serious)
It starts with cells that make the pigment melanin. Because it forms on the skin, patients are usually the first to spot the cancers on the skin.
This type is also called exocrine cancer. The cancer cells form in the tissues of the pancreas.
This type usually occurs in men over 50 years of age and the risk increases as you grow older. It develops in tissues of the prostate (a gland in the male reproductive system found below the bladder and in front of the rectum).
It is commonly known as cancer of the blood. It starts in blood-forming tissue such as the bone marrow and causes large numbers of blood cells to be produced and enter the bloodstream.
Cancer experts have put them into 4 types: papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic thyroid cancer. This cancer forms in the thyroid gland. The thyroid is located at the base of the throat.
The rest include Colon and Rectal Cancer, Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, Endometrial Cancer
Cancer Testing and Diagnosis
Your doctor will analyze the symptoms, your medical history, and do a physical examination. He will make a recommendation for further tests at the lab.
At the lab, you may have x-rays and blood tests taken and possibly scans. A biopsy may also be needed. The biopsy sample is then analysed in a laboratory and the cells examined so that the doctors can see exactly what type of cancer it is and whether it is likely to grow slowly or more quickly.
Below is an example of an x-ray of a lung with cancer.
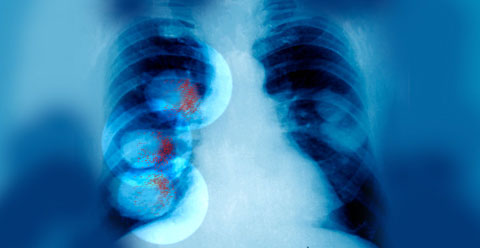
Early diagnosis
 Thousands of people beat cancer every year. This is because when cancer’s diagnosed at an early stage, treatment is often simpler and more likely to be effective. So finding cancer early can make a real difference.
Thousands of people beat cancer every year. This is because when cancer’s diagnosed at an early stage, treatment is often simpler and more likely to be effective. So finding cancer early can make a real difference.
 Sometimes, people avoid the doctor because they’re worried about what the doctor might find. Remember that there is massive improvement in the way cancer is tested and diagnosed. There is great improvement in treatment too, so there is no need to be frightened. It is better to see your doctor earlier rather than later.
Sometimes, people avoid the doctor because they’re worried about what the doctor might find. Remember that there is massive improvement in the way cancer is tested and diagnosed. There is great improvement in treatment too, so there is no need to be frightened. It is better to see your doctor earlier rather than later.
 The number of people who die from cancer has been falling overall.
The number of people who die from cancer has been falling overall.
 Half the people diagnosed with cancer today will still be alive in five years’ time. And more than 40% will still be alive in ten years’ time. The average ten-year survival rate for cancer has doubled over the past 30 years.
Half the people diagnosed with cancer today will still be alive in five years’ time. And more than 40% will still be alive in ten years’ time. The average ten-year survival rate for cancer has doubled over the past 30 years.
 For many types of cancer, including prostate cancer and melanoma skin cancer the number of people who survive has improved greatly.
For many types of cancer, including prostate cancer and melanoma skin cancer the number of people who survive has improved greatly.
 Death rates from three of the UK’s most common cancers - breast, bowel and male lung cancer - have dropped to their lowest level for almost 40 years.
Death rates from three of the UK’s most common cancers - breast, bowel and male lung cancer - have dropped to their lowest level for almost 40 years.
 More than nine out of ten men with testicular cancer are now effectively cured.
More than nine out of ten men with testicular cancer are now effectively cured.
 And now more than three quarters of children with cancer survive, compared with only a quarter back in the 60s.
And now more than three quarters of children with cancer survive, compared with only a quarter back in the 60s.
 Even for those cancers where survival overall is poor, the chances of surviving are better the earlier the stage at which the cancer’s diagnosed.
Even for those cancers where survival overall is poor, the chances of surviving are better the earlier the stage at which the cancer’s diagnosed.
So if you notice anything unusual about your body, or have one of the warning signs or symptoms, it’s really important to talk to your doctor about it. It may not be anything to worry about, in which case you will have nothing to lose. But if it’s something serious, you could have everything to gain.
Your doctor will analyze the symptoms, your medical history, and do a physical examination. He will make a recommendation for further tests at the lab.
At the lab, you may have x-rays and blood tests taken and possibly scans. A biopsy may also be needed. The biopsy sample is then analysed in a laboratory and the cells examined so that the doctors can see exactly what type of cancer it is and whether it is likely to grow slowly or more quickly.
Below is an example of an x-ray of a lung with cancer.

Early diagnosis
So if you notice anything unusual about your body, or have one of the warning signs or symptoms, it’s really important to talk to your doctor about it. It may not be anything to worry about, in which case you will have nothing to lose. But if it’s something serious, you could have everything to gain.
Cancer signs and symptoms
When cancer's found at an early stage, treatment is often easier and more likely to be successful. So finding cancer sooner rather than later can make a real difference.
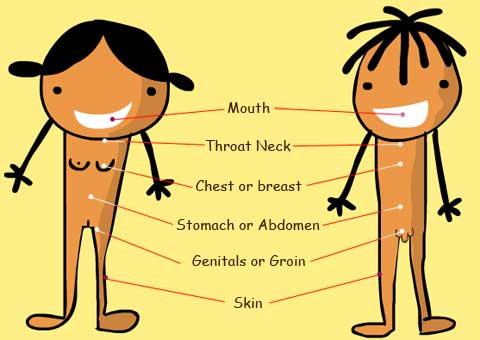
Illustration of some common areas that cancer usually forms
Symptoms of cancer vary based on the type of cancer. As cancer progresses to an advanced stage, common symptoms can include weight loss, fever, and fatigue. Look out for these:
General
 An unusual lump or swelling anywhere on your body
An unusual lump or swelling anywhere on your body
 Unusual and unexplained heavy sweating at night
Unusual and unexplained heavy sweating at night
 Unexplained weight loss
Unexplained weight loss
Skin
 A change in the size, shape or colour of a patch of skin
A change in the size, shape or colour of a patch of skin
 A sore that’s not healing for many weeks
A sore that’s not healing for many weeks
Mouth
 Tongue or mouth sore that’s lasted for more that 3 weeks
Tongue or mouth sore that’s lasted for more that 3 weeks
Throat and Neck
 An unusual swelling or lump
An unusual swelling or lump
 A croaky, rough voice that is lasting for many weeks
A croaky, rough voice that is lasting for many weeks
 Difficulty in swallowing
Difficulty in swallowing
Chest
 Breathlessness
Breathlessness
 Unexplained coughing for more that three weeks
Unexplained coughing for more that three weeks
 Coughing up blood
Coughing up blood
Genitals
 Blood in urine
Blood in urine
 Problems passing urine
Problems passing urine
 (ladies) Bleeding from the vagina after sex, after menopause or between periods
(ladies) Bleeding from the vagina after sex, after menopause or between periods
Bottom Area
 Blood in your bowel motions
Blood in your bowel motions
 A noticeable change or frequency in bowel motions
A noticeable change or frequency in bowel motions
When cancer's found at an early stage, treatment is often easier and more likely to be successful. So finding cancer sooner rather than later can make a real difference.

Illustration of some common areas that cancer usually forms
Symptoms of cancer vary based on the type of cancer. As cancer progresses to an advanced stage, common symptoms can include weight loss, fever, and fatigue. Look out for these:
General
Skin
Mouth
Throat and Neck
Chest
Genitals
Bottom Area
Treatment of Cancer
There are four standard methods of treatment for cancer: surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy), and immunotherapy/biologic therapy. An oncologist will provide the patient with cancer treatment options after diagnosis of the cancer. They are the experts and can give you good advice, but ultimately, the patient has to decide what kind of treatment they want. Some treatment options can be used by itself, with surgery, with radiotherapy or together with others.
 Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (chemo) is a drug treatment aimed to cure cancer or relieve any symptoms cancer can cause. Chemotherapy either kills cancer cells or stops them dividing. Your doctor will discuss the best options with you and your family if you wish. This is administered in many ways: by injections, infusion (drip), continuous infusion (usually carried around as you go about your daily business), as tablets that you swallow, or as ointment to be applied to skin. There are various types of cancers and so naturally, chemo treatments will vary.
 Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is a way of treating or managing cancer usingradiation. It works by damaging cells in the area being treated - over half of cancer patients will receive radiotherapy at some point in their treatment. Radiotherapy can be given as teletherapy (also known as external beam radiotherapy), when a beam of radiation is aimed at the area to be treated from a machine located away from the patient.
 Immunotherapy/biologic therapy
Immunotherapy/biologic therapy
Immunotherapy is also sometimes called biologic therapy or biotherapy. It is treatment that uses certain parts of the immune system to fight diseases such as cancer. This can be done in a couple of ways: Stimulating your own immune system to work harder or smarter to attack cancer cells or Giving your immune system components, such as man-made immune system proteins, or by training the immune system to attack some part of cancer cells specifically.
CARE For Patients

It is very important that people with cancer are given full respect, love and attention to help them recover well. You should work closely with the doctor (or nurse), and assist with the treatment programme. If there is a lot of money involved and you think you need a bit of help, discuss with your doctor for charity organizations to come in. These charity organizations may also have special skills in helping people, children and families with cancer members.
There are four standard methods of treatment for cancer: surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy), and immunotherapy/biologic therapy. An oncologist will provide the patient with cancer treatment options after diagnosis of the cancer. They are the experts and can give you good advice, but ultimately, the patient has to decide what kind of treatment they want. Some treatment options can be used by itself, with surgery, with radiotherapy or together with others.
Chemotherapy (chemo) is a drug treatment aimed to cure cancer or relieve any symptoms cancer can cause. Chemotherapy either kills cancer cells or stops them dividing. Your doctor will discuss the best options with you and your family if you wish. This is administered in many ways: by injections, infusion (drip), continuous infusion (usually carried around as you go about your daily business), as tablets that you swallow, or as ointment to be applied to skin. There are various types of cancers and so naturally, chemo treatments will vary.
Radiotherapy is a way of treating or managing cancer usingradiation. It works by damaging cells in the area being treated - over half of cancer patients will receive radiotherapy at some point in their treatment. Radiotherapy can be given as teletherapy (also known as external beam radiotherapy), when a beam of radiation is aimed at the area to be treated from a machine located away from the patient.
Immunotherapy is also sometimes called biologic therapy or biotherapy. It is treatment that uses certain parts of the immune system to fight diseases such as cancer. This can be done in a couple of ways: Stimulating your own immune system to work harder or smarter to attack cancer cells or Giving your immune system components, such as man-made immune system proteins, or by training the immune system to attack some part of cancer cells specifically.
CARE For Patients

It is very important that people with cancer are given full respect, love and attention to help them recover well. You should work closely with the doctor (or nurse), and assist with the treatment programme. If there is a lot of money involved and you think you need a bit of help, discuss with your doctor for charity organizations to come in. These charity organizations may also have special skills in helping people, children and families with cancer members.
Cancer Prevention Tips
Experts estimate that more than 4 in 10 cancer cases could be prevented. A few simple lifestyle changes, can drastically reduce your risk of many types of cancer.
 Avoid Smoking and Exposure to Smoke
Avoid Smoking and Exposure to Smoke
Smoking is responsible for many cancers. Second-hand smoking is also dangerous as they contain carcinogens.
 Practice Sun Safety and
Practice Sun Safety and
Recognize When Skin Changes Occur

Skin cancers are the most preventable. Skin cancer is caused by Ultra Violet Rays (UV Rays) from the sun. Wearing sunscreen, avoiding mid-day sun, wearing protective clothing when outdoors, staying away from tanning beds and general protection from direct sun rays will zero any risk of skin cancer.
 Eat Fresh Fruits and Veggies
Eat Fresh Fruits and Veggies
Fruits and vegetables (especially brightly coloured) contain antioxidants, which help repair our damaged cells. Studies show that dark fruits, like blueberries and grapes, may also have anti-cancer properties. Cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli and cauliflower appear to pack a powerful punch at preventing cancer. Other cruciferous vegetables include bok choy, Brussel sprouts and cabbage.
 Limit Red Meat and Animal Fat
Limit Red Meat and Animal Fat
Animal fat increases the risk for several types of cancer, particularly colon cancer. Chose fish and poultry over red meat, as they have less fat. Fatty foods also cause obesity, which is a risk factor for many types of cancer too.
 Limit Your Alcohol Intake
Limit Your Alcohol Intake
Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol regularly increases your risk factor for many types of cancer. Two simple ways include: Alcohol is converted into a toxic chemical called acetaldehyde. This chemical can cause cancer by damaging DNA and stopping our cells from repairing this damage. It can damage the cells of the liver, causing a disease called cirrhosis. Cirrhosis makes you more vulnerable to liver cancer.
Experts estimate that more than 4 in 10 cancer cases could be prevented. A few simple lifestyle changes, can drastically reduce your risk of many types of cancer.
Smoking is responsible for many cancers. Second-hand smoking is also dangerous as they contain carcinogens.
Recognize When Skin Changes Occur

Skin cancers are the most preventable. Skin cancer is caused by Ultra Violet Rays (UV Rays) from the sun. Wearing sunscreen, avoiding mid-day sun, wearing protective clothing when outdoors, staying away from tanning beds and general protection from direct sun rays will zero any risk of skin cancer.
Fruits and vegetables (especially brightly coloured) contain antioxidants, which help repair our damaged cells. Studies show that dark fruits, like blueberries and grapes, may also have anti-cancer properties. Cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli and cauliflower appear to pack a powerful punch at preventing cancer. Other cruciferous vegetables include bok choy, Brussel sprouts and cabbage.
Animal fat increases the risk for several types of cancer, particularly colon cancer. Chose fish and poultry over red meat, as they have less fat. Fatty foods also cause obesity, which is a risk factor for many types of cancer too.
Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol regularly increases your risk factor for many types of cancer. Two simple ways include: Alcohol is converted into a toxic chemical called acetaldehyde. This chemical can cause cancer by damaging DNA and stopping our cells from repairing this damage. It can damage the cells of the liver, causing a disease called cirrhosis. Cirrhosis makes you more vulnerable to liver cancer.
Just 30 minutes of moderate activity a day, five days a week, can have a positive effect on your health. And the more active you are, the more you can reduce your risk of cancer.
One good reason is, the sugar-regulating hormone insulin is known to lead to faster cell growth and division and to increase women's risk of breast cancer recurrence. Exercise lowers levels of this hormone.
Knowing your family history of cancer is important to properly assess your risk factor for certain types of cancer. Cancers like breast, colon, ovarian, and possibly other types can be hereditary. This means it is important to know your family history, and tell your doctor if you are in a high risk family line.
Exposed to in Your Work Environment
Chemicals in the workplace may increase your risk of developing many types of cancer, including kidney cancer and bladder cancer. Avoid exposure to fumes, dust, chemicals, Gasoline, diesel exhaust, arsenic, beryllium, vinyl chloride, nickel chromates, coal products, mustard gas, and chloromethyl. They are all carcinogens. If your parents work in environments like that, they need to talk to the employer about limiting exposure.
Surprised? Unsafe sex can result in the infection of the human papillomairus (HPV), a known cause for cervical cancer and a risk factor for many other types of cancer. HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection that is spread through sexual, skin-to-skin contact. As a young person, it is important to stay away from early sexual activity until you are mature enough (or married) to do so. This way, you can minimise your exposure to sexually transmitted infections.
Cancer screening tests can be useful not only in detecting cancer, but also helping prevent it. Tests like the colonoscopy and Pap smear can detect abnormal cellular changes before they turn cancerous. It is effective when done regularly.
Other cancer screening tests are available and may be useful for early detection, but not necessarily cancer prevention. Prostate cancer screening through digital rectal exams and PSA tests can help detect prostate cancer early. Mammograms and other imaging tools are also recommended to detect breast cancer in women.
Cancer Factsheet
 Why is cancer cases on the rise in the developing world?
Why is cancer cases on the rise in the developing world?
Dr. Otis Brawley, a Cancer Expert explains that there are two reasons. The 'good' one is that, the population is getting healthier and people are living longer to reach 60's and 70's. The 'bad' one is that, bad habits like tobacco smoking, high calorie diets and obesity in the US and Europe are being exported to the developing world.
Dr. Otis Brawley, a Cancer Expert explains that there are two reasons. The 'good' one is that, the population is getting healthier and people are living longer to reach 60's and 70's. The 'bad' one is that, bad habits like tobacco smoking, high calorie diets and obesity in the US and Europe are being exported to the developing world.
In the USA, 33% of all cancers are related to tobacco smoking and 28%-29% are related to obesity, high calorie intake and lack of physical activity. Source—CNN
 Over 1M Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer each year.
Over 1M Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer each year.
 In the UK, more than one in three people will develop cancer at some point in their lives. Every year, around 309,500 people are diagnosed with the disease.
In the UK, more than one in three people will develop cancer at some point in their lives. Every year, around 309,500 people are diagnosed with the disease.
 More than 30% of cancers could be cured if detected early and treated adequately.
More than 30% of cancers could be cured if detected early and treated adequately.
 More than 30% of cancer could be prevented, mainly by not using tobacco, having a healthy diet, being physically active and preventing infections that may cause cancer.
More than 30% of cancer could be prevented, mainly by not using tobacco, having a healthy diet, being physically active and preventing infections that may cause cancer.
 One fifth of all cancers worldwide are caused by a chronic infection, for example human papillomavirus (HPV) causes cervical cancer and hepatitis B virus (HBV) causes liver cancer.
One fifth of all cancers worldwide are caused by a chronic infection, for example human papillomavirus (HPV) causes cervical cancer and hepatitis B virus (HBV) causes liver cancer.
 Worldwide, the 5 most common types of cancer that kill women are (in the order of frequency): breast, lung, stomach, colorectal and cervical.
Worldwide, the 5 most common types of cancer that kill women are (in the order of frequency): breast, lung, stomach, colorectal and cervical.
 About 70% of all cancer deaths occur in low and middle-income countries.
About 70% of all cancer deaths occur in low and middle-income countries.
 In 2008, 7.6 million people died of cancer - 13% of all deaths worldwide.
In 2008, 7.6 million people died of cancer - 13% of all deaths worldwide.
 There are more than 200 types of cancers; any part of the body can be affected.
There are more than 200 types of cancers; any part of the body can be affected.
 Every year in the UK, over 40,000 men are diagnosed with prostate cancer. Although it is one of the more treatable types of cancer, particularly if diagnosed early, one man dies every hour from it, says Prostate Cancer UK. (via BBC)
Every year in the UK, over 40,000 men are diagnosed with prostate cancer. Although it is one of the more treatable types of cancer, particularly if diagnosed early, one man dies every hour from it, says Prostate Cancer UK. (via BBC)
0 comments:
Post a Comment